24.10.2022
Sticky cell fingers help keep breast tumours contained
Researchers have identified that finger-like cellular extensions called filopodia contribute to building a barrier surrounding breast tumours.
At the early stage of breast cancer, malignant cells are imprisoned by a tissue barrier called a basement membrane that stops them from disseminating into other parts of the body. This early disease stage is typically not life-threatening, as surgery can remove the tumour. However, breast cancer can become lethal if it spreads and forms metastases.
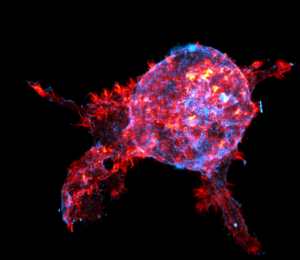
To escape and spread, tumour cells first need to break through their most proximal barrier, the basement membrane. Researchers at Åbo Akademi University and the University of Turku, Finland, have discovered that cellular structures called filopodia help preserve the basement membrane surrounding the tumour, blocking their escape.
“These results are very surprising as we previously thought that these cancer cells’ sticky fingers were only used to invade nearby tissues. Now we find that these structures can also help contain the tumour,” says InFLAMES Group Leader, Prof. Johanna Ivaska, University of Turku.
These sticky fingers are generated by a protein called Myosin-10. The research teams led by Prof. Ivaska, Dr. Emilia Peuhu, Docent at the Institute of Biomedicine at the University of Turku, and Dr. Guillaume Jacquemet, Associate Professor of Cell Biology, Åbo Akademi University, found that cancer cells lacking Myosin-10 cannot build and maintain their surrounding barrier, the basement membrane, making it easier for cancer cells to escape.
“Remove Myosin-10, and the tumours are clearly more aggressive. Their basement membrane is almost completely gone, and they spread more freely to the surrounding tissue”, says Dr. Peuhu.
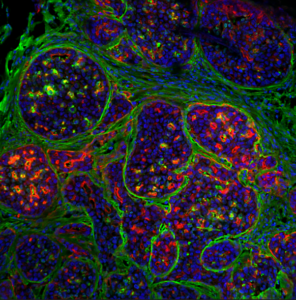
For several years, the Ivaska and Jacquemet teams have focused their efforts on understanding how cancer cells use filopodia to move and invade surrounding tissue. Their previous findings highlighted that filopodia are used by cancer cells to disseminate once they escape the primary tumour. Now the teams found that filopodia have an opposite role at the early stage of the disease.
“We’ve been looking into developing anti-filopodia strategies to treat cancers, but our new results clearly emphasize that targeting filopodia or Myosin-10 too early could actually make things worse”, says Dr. Jacquemet.
The teams and their collaborators are now assessing how filopodia regulate basement membranes’ assembly.
The findings were published in the journal Developmental Cell on 24 October 2022.
For more information, please contact:
Dr. Johanna Ivaska,
Professor, Turku Bioscience, University of Turku
E-mail: johanna.ivaska@utu.fi
Phone: +358 29 450 2260
Dr. Guillaume Jacquemet,
Associate Professor of Cell Biology, Åbo Akademi University
E-mail: guillaume.jacquemet@abo.fi
Phone: +358 503235606
Dr. Emilia Peuhu,
Docent and Academy Research Fellow, Institute of Biomedicine, University of Turku
E-mail: emilia.peuhu@utu.fi
Phone: +358 29 450 2259